Accessing Azure App Services Using Azure Ad Bearer Token
- 17 Mar 2017
Here are some simplified instructions on how to setup and use Azure Active Directory authentication for Azure App Services and code that will allow an application to use a Bearer Token to access that app.
Review
Simply put, the OAuth Bearer Token simply identifies the app that is calling an Azure Active Directory registered application. The calling application requests a Token from AD by providing some information to include the Client Secret and Application ID of the app that will be calling the target app (the app that will use the token) as well as the Application ID of the application you wish to call. The client secret is the key that you want to protect and keep ‘secret’.
Walkthrough
Register the target app you want to call in Azure AD and get the Application ID. No client secret required.
Simply click on the application in the portal and enable Azure AD authentication (express) and save.
Copy the Application ID. After the app is updated go back into the Azure Active Authentication and click on the Advanced button. This will allow you to copy the Application ID:
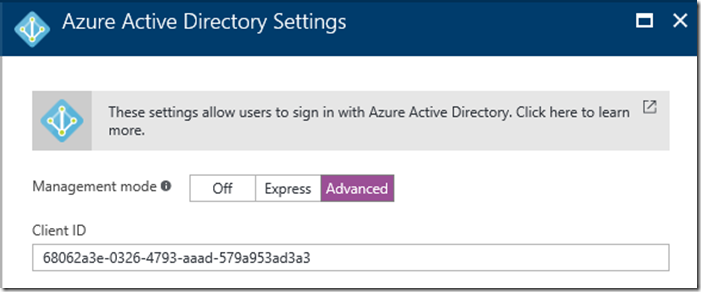
###
Register the client app you want to call from in Azure AD and get the Application ID, and generate a Client Secret Key
Simply click on the application in the portal and enable Azure AD authentication (express) and save.
You now need to go to the application registered in Azure AD and get the Application ID and generate a Client Secret. Copy the Application ID and Client Secret of this client app to use later like you did in the previous step.
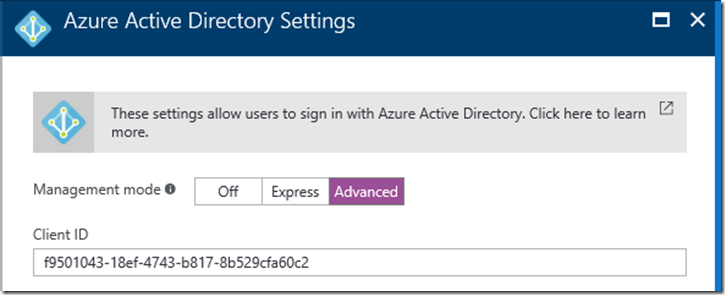
Generate a client Secret by going to Azure Active Directory in the portal. Search for the Client app:
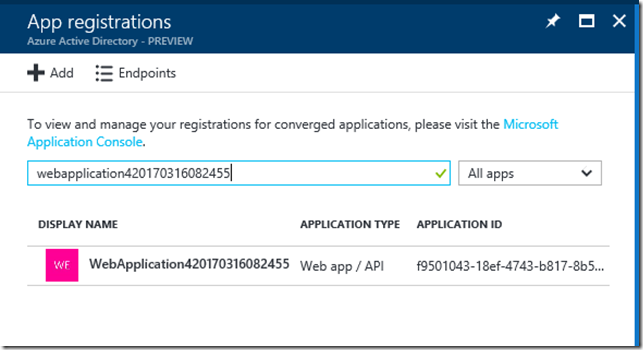
In Settings choose Keys:
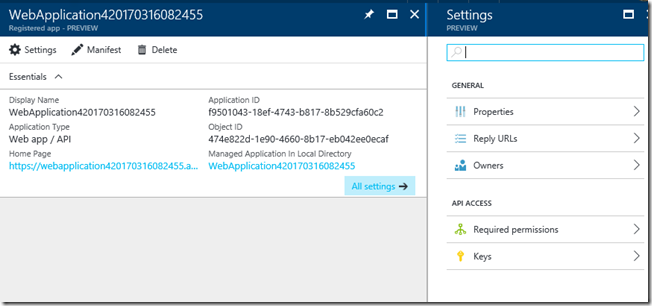
In Keys create a New Key (name it whatever you want) and Save:
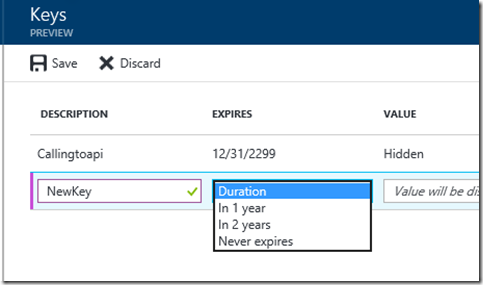
Important. When you save you need to copy the Value for later as you cannot come back and get it. This is the Client Secret.
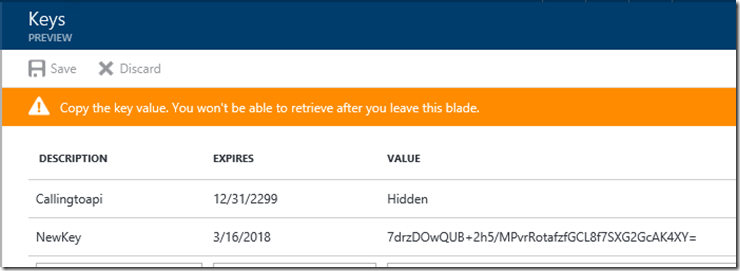
Note: You can always generate a new secret if you forget or lose it.
Create code to get a Bearer token from Azure AD and use this token to call the Target app
Now you simply need to use the values from above to request a token and make a request using that token in the Authorization header.
Here is some sample code. First the ServicePrinciple class is used to build and get the token. I am using the latest ADAL library we provide (Microsoft.IdentityModel.Clients.ActiveDirectory ver 3.13.8:
public static class ServicePrincipal { /// <summary> /// The variables below are standard Azure AD terms from our various samples /// We set these in the Azure Portal for this app for security and to make it easy to change (you can reuse this code in other apps this way) /// You can name each of these what you want as long as you keep all of this straight /// </summary> static string authority = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["ida:Authority"]; // the AD Authority used for login. For example: https://login.microsoftonline.com/myadnamehere.onmicrosoft.com static string clientId = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["ida:ClientId"]; // the Application ID of this app. This is a guid you can get from the Advanced Settings of your Auth setup in the portal static string clientSecret = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["ida:ClientSecret"]; // the key you generate in Azure Active Directory for this application static string resource = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["ida:Resource"]; // the Application ID of the app you are going to call. This is a guid you can get from the Advanced Settings of your Auth setup for the targetapp in the portal /// <summary> /// wrapper that passes the above variables /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> static public async Task<AuthenticationResult> GetS2SAccessTokenForProdMSAAsync() { return await GetS2SAccessToken(authority, resource, clientId, clientSecret); } static async Task<AuthenticationResult> GetS2SAccessToken(string authority, string resource, string clientId, string clientSecret) { var clientCredential = new ClientCredential(clientId, clientSecret); AuthenticationContext context = new AuthenticationContext(authority, false); AuthenticationResult authenticationResult = await context.AcquireTokenAsync( resource, // the resource (app) we are going to access with the token clientCredential); // the client credentials return authenticationResult; } }
And then using this class my code to fetch data from the Target resource:
protected async void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Normally you would use a single Global HttpClient per MS guidance // but for demo purposes... Just create one inline HttpClient client = new HttpClient(); // This is an Aspx page so clearing anything already written in the buffer Response.Clear(); try { // get the token var token = await ServicePrincipal.GetS2SAccessTokenForProdMSAAsync(); // set the auth header with the aquired Bearer token client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Authorization = new AuthenticationHeaderValue("Bearer",token.AccessToken); // make the call to the resource requiring auth! var resp = await client.GetAsync("https://jsandersapicall.azurewebsites.net/"); // do something with the response Response.Write(resp.StatusCode.ToString()); } catch (Exception ex) { // important to log the exception if any because it will tell you what went wrong Response.Write(ex.Message); } // write page out Response.Flush(); }
Conclusion
This is a very compact sample that can be used as a checklist. It eliminated a lot of the information in our documentation here: Service principal authentication for API Apps in Azure App Service
Drop me a note if you found this useful!